Vitamin B7 (Biotin) Blood Test – Functions, Deficiency, Symptoms, Normal Levels & Importance
Introduction
The Vitamin B7 (Biotin) blood test measures the amount of biotin circulating in the bloodstream. Vitamin B7, also known as biotin or Vitamin H, is a water-soluble member of the B-complex family. It plays an essential role in energy metabolism and supports the normal function of the skin, hair, nails, nervous system, and multiple cellular processes.
Although biotin is commonly associated with cosmetic health, its biological importance extends well beyond appearance. It participates in metabolic pathways that allow the body to process nutrients efficiently and supports normal nervous system activity and cell growth. Because the body does not store biotin in significant amounts, testing becomes useful when deficiency is suspected or when high supplemental intake may be influencing laboratory results.
What is Vitamin B7 (Biotin)?
Vitamin B7 is a water-soluble vitamin that functions as a coenzyme in several critical metabolic reactions. These reactions are involved in breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and certain amino acids so that cells can generate energy.
As a water-soluble nutrient, biotin is cleared from the body relatively quickly. When intake or absorption is reduced, levels may decline over time. Low availability can affect tissues with high metabolic activity, including the skin, hair follicles, and nervous system.
Where is Vitamin B7 Produced in the Body?
The human body does not produce sufficient amounts of biotin on its own. Small quantities are synthesized by intestinal bacteria, but this contribution is limited and does not meet daily requirements.
Most biotin comes from external sources. After absorption, it circulates in the blood and is delivered to tissues where it supports metabolic and cellular functions. Under normal conditions, dietary intake maintains stable levels unless absorption or metabolic factors interfere.
Main Functions and Importance of Vitamin B7
Vitamin B7 supports several interconnected biological functions.
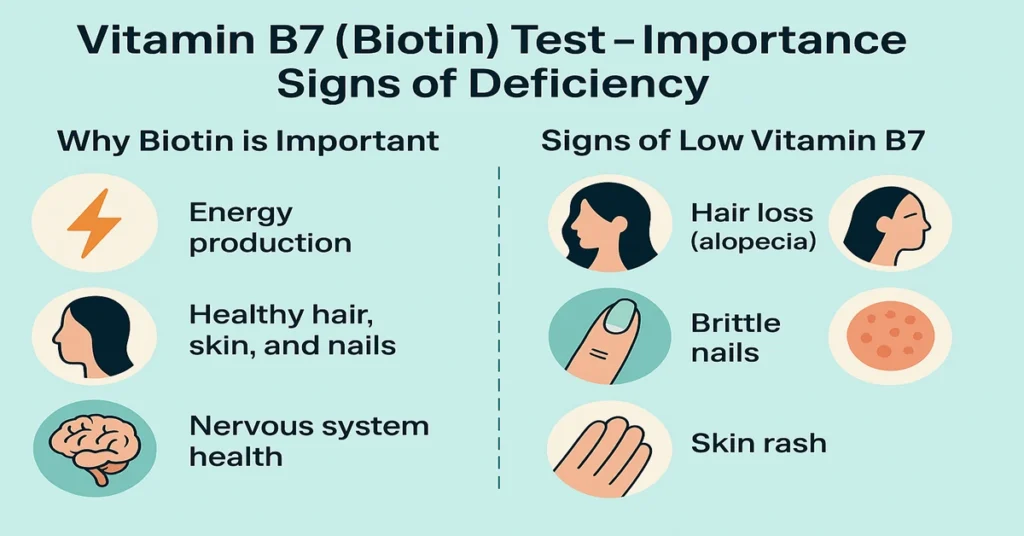
Energy Production
Biotin acts as a coenzyme in metabolic pathways that convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable cellular energy. When levels are reduced, metabolic efficiency may decline, contributing to generalized tiredness.
Hair, Skin, and Nail Integrity
Biotin contributes to the production of keratin, a structural protein essential for hair strength, skin integrity, and nail firmness. Reduced levels are often first noticed through changes in these tissues.
Nervous System Function
Biotin supports normal nerve signaling and brain cell communication. Low availability may be associated with changes in mood, cognitive clarity, or sensory function.
Blood Sugar and Glucose Metabolism
Biotin plays a role in enzymes involved in glucose metabolism, supporting balanced energy availability in the body.
Gene Regulation and Cell Growth
Vitamin B7 participates in DNA-related processes, including gene expression and cell division, making it important for tissue maintenance and growth.
Causes of Low Vitamin B7 Levels
Biotin deficiency is uncommon but may develop under specific conditions.
Common Causes
Reduced intake, prolonged fasting, chronic alcohol use, long-term antibiotic therapy, and certain genetic or metabolic conditions can lower biotin availability. Increased physiological demand, such as during pregnancy, may also contribute. In many cases, deficiency develops gradually rather than suddenly.
Symptoms of Vitamin B7 Deficiency
Low biotin levels most commonly affect the skin, hair, nails, and nervous system.
Individuals may notice hair thinning, brittle nails, or skin changes, often around the face. Fatigue, low mood, or sensory symptoms such as tingling or numbness may also occur. In infants, deficiency may present with neurological or developmental signs. Symptoms often overlap with other nutrient deficiencies, making laboratory testing helpful for clarification.
Causes of High Vitamin B7 Levels
Elevated biotin levels are almost always related to external intake.
High concentrations are most often seen in people using biotin-containing supplements, particularly high-dose formulations. Dietary sources alone rarely cause elevated blood levels.
Symptoms of High Vitamin B7 (Toxicity)
Biotin itself is not known to cause direct toxicity. However, high circulating levels can interfere with certain laboratory tests.
This interference may lead to misleading results in tests such as thyroid panels, cardiac markers, and some hormone assays. For this reason, biotin intake is an important consideration when interpreting laboratory results.
Reference Range (Normal Levels)
Reference ranges for biotin may vary slightly depending on laboratory method.
Values within the established range are considered adequate. Lower values suggest reduced availability, while higher values usually reflect recent supplementation rather than clinical toxicity.
Sample Type and Test Method
Sample Type: Blood sample (serum or plasma)
Purpose: Measurement of circulating biotin concentration
Fasting: Not typically required
Testing Method: High-performance laboratory techniques such as HPLC or immunoassay
Results are generally available within one to two days.
Test Preparation
Preparation is usually minimal. Temporary discontinuation of biotin-containing supplements before testing may be advised to reduce analytical interference. Informing the healthcare provider about supplement use helps ensure accurate interpretation.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical review is appropriate if symptoms such as unexplained hair loss, skin changes, sensory discomfort, fatigue, or mood changes persist. Individuals with abnormal thyroid or cardiac test results while using biotin supplements should also seek evaluation. In some cases, further testing may be recommended to assess overall nutritional or metabolic status.
Important Word Explanations
- Biotin / Vitamin B7: A water-soluble B-complex vitamin essential for metabolism and cellular health
- Avidin: A protein found in raw egg whites that binds biotin and reduces absorption
- Biotinidase Deficiency: A rare genetic condition that impairs biotin recycling
- Neuropathy: Nerve dysfunction causing tingling or numbness
- Hypotonia: Reduced muscle tone, particularly noted in infants
~END~
Related Posts
None found