Functions, Importance and Normal Range of Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are a key part of the immune system and help the body fight infections, viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells. In routine OPD and laboratory practice, lymphocyte values are often reviewed when someone reports repeated infections, slow recovery, or unexplained fatigue. These cells quietly work in the background, but when their levels move outside the normal range, the immune balance can be affected.
Understanding what lymphocytes do, why they matter, and how their normal ranges change with age and conditions helps patients and students read reports with more confidence. This article explains their functions, importance, normal ranges, and how doctors usually interpret high or low values.
What Lymphocytes Do in the Body
Lymphocytes protect the body by identifying threats and coordinating long-term immune defense. They circulate through the blood, lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow, constantly monitoring for infections or abnormal cells.
There are three main types of lymphocytes, each with a distinct role. T cells directly attack infected or abnormal cells and help regulate immune responses. B cells produce antibodies that help the body recognize and remember infections. Natural Killer (NK) cells destroy virus-infected cells and early cancer-like cells. Although their functions differ, all three work together to maintain strong immunity.
Why Lymphocytes Are Important
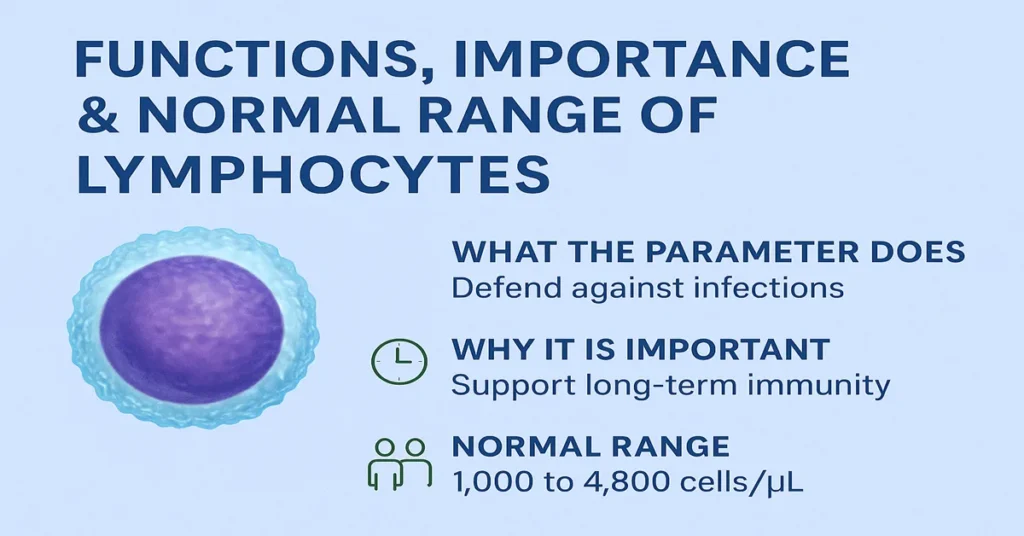
Lymphocytes are essential for a balanced immune system. When levels are adequate, the body can respond effectively to infections and build long-term protection after illness or vaccination. When levels fall too low, infections may occur more often or take longer to resolve. When levels are persistently high, it usually means the immune system is being continuously stimulated.
Clinically, lymphocyte levels act as signals. They help doctors understand whether the immune system is under stress, recovering from infection, or reacting to a chronic condition.
Role of Lymphocytes in the Body
Beyond basic infection control, lymphocytes perform several important roles. They provide immune surveillance by constantly scanning for harmful or abnormal cells. During infection, they move toward affected tissues to limit spread. B cells support antibody production, which prevents repeat infections. Lymphocytes also help regulate inflammation so that immune responses do not cause unnecessary tissue damage. Effective vaccine responses depend heavily on healthy lymphocyte function.
Normal Range of Lymphocytes
Lymphocyte levels vary with age, physiological state, and overall health. Doctors always interpret values in context rather than relying on a single number.
General adult range
In most laboratories, the adult lymphocyte range is about 1,000 to 4,800 cells per microliter. Slight variation between labs is normal.
Age-wise normal ranges
Infants naturally have higher lymphocyte levels because their immune system is still developing. Children continue to show higher and wider ranges that gradually settle as they approach adolescence. Teenagers begin to show adult-like values. In older adults, slightly lower ranges are common and often reflect age-related immune changes rather than disease.
Gender-wise ranges
Differences between men and women are usually small and not clinically significant. Mild fluctuations may be seen in women during certain hormonal phases, such as the menstrual cycle.
Pregnancy lymphocyte ranges
Pregnancy brings natural immune adjustments. Lymphocyte levels may decrease slightly, especially in early pregnancy, as the body adapts to protect the developing fetus. These changes are considered normal unless accompanied by symptoms or extreme values.
When Abnormal Levels Become Risky
Both low and high lymphocyte levels can be concerning depending on severity and persistence.
Low lymphocytes (lymphocytopenia)
Low levels may be seen with viral infections, stress, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune conditions, or certain medications. Mild reductions are common and often temporary. Persistent low counts increase susceptibility to infections and warrant evaluation.
High lymphocytes (lymphocytosis)
High levels usually indicate infection, inflammation, recovery from illness, or immune stimulation. Persistent elevations may be seen in chronic infections or autoimmune conditions. Rarely, very high or steadily rising counts prompt evaluation for blood-related disorders.
Test Preparation for Lymphocyte Test
Lymphocyte levels are usually measured as part of a CBC test. Fasting is not usually required. Normal hydration is advised. Avoid smoking and alcohol before the test, and inform the doctor about medications. Recent fever or infection should be mentioned, as it can temporarily affect results.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical advice is important if lymphocyte levels remain abnormal on repeated tests, if infections are frequent or severe, or if there are symptoms such as persistent fever, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, or long-lasting cough or sore throat. Early evaluation helps clarify whether the change is temporary or needs monitoring.
Important Word Explanations
| Term | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | White blood cells that protect the body from infections and abnormal cells. |
| Antibodies | Proteins made by B cells that help neutralize germs. |
| Immune system | The body’s defense system against infections and disease. |
| Lymphocytosis | A condition where lymphocyte levels are higher than normal. |
| Lymphocytopenia | A condition where lymphocyte levels are lower than normal. |
| Chronic | A condition that lasts a long time or keeps recurring. |
People Also Ask
Is an abnormal lymphocyte count always serious?
Not always. Mild changes are common and often temporary.
Can lymphocyte levels change during infection or recovery?
Yes. Levels may rise during recovery from infection or fall briefly during illness.
Does a high lymphocyte count always mean disease?
No. It often reflects immune activity rather than a specific disease.
When do doctors usually worry about lymphocyte levels?
Concern increases when levels are very high or low, persistent, or linked with symptoms.
Is repeat testing common for lymphocyte abnormalities?
Yes. Doctors often repeat CBC tests to observe trends over time.
Can someone feel normal with abnormal lymphocyte levels?
Yes. Many people have no symptoms, especially when changes are mild or short-lived.
~END~

Useful info. Fortunate me I discovered your site unintentionally,
and I am shocked why this accident did not took place earlier!
I bookmarked it.