Platelets: Causes of High Platelet Levels and How to Reduce Them Naturally
Platelets are small but essential blood cells that play a key role in stopping bleeding and supporting healing. In routine laboratory and OPD practice, platelets are often described as the body’s emergency repair cells—they rush to any injury and help form clots so blood loss is controlled.
However, when platelet levels rise more than normal, a condition known as thrombocytosis, the balance shifts. Instead of helping, excess platelets can make the blood more prone to clotting. Most cases seen in daily practice are reactive or secondary, meaning they are a response to another condition rather than a primary blood disease.
This article explains what high platelet levels mean, why they happen, how doctors usually interpret them, and what natural, supportive steps help bring levels back toward normal—without turning this into a treatment guide.
What Are High Platelet Levels? (Short Overview)
Platelet count is measured as part of a CBC (Complete Blood Count) test.
- Normal range: 150,000 – 450,000 per microliter
- High platelet count: Above 450,000 per microliter
Clinically, high platelet counts are grouped into two broad types:
- Secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis:
The most common type. Platelets rise as a reaction to infection, inflammation, iron deficiency, surgery, or dehydration. - Primary thrombocytosis:
Rare. Caused by bone marrow disorders where platelets are produced excessively without an external trigger.
In everyday lab practice, the majority of patients fall into the secondary category, which often improves once the underlying cause settles.
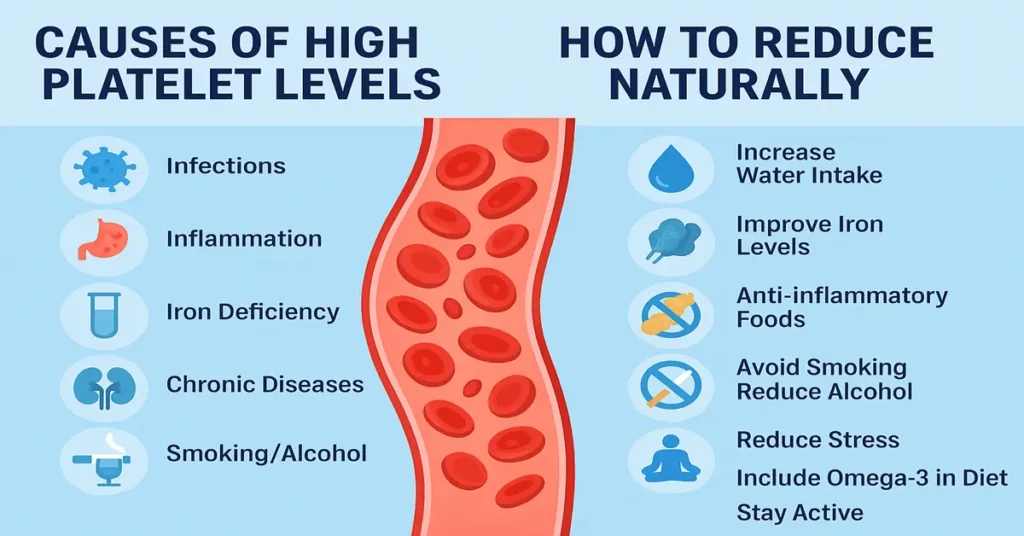
Medical Causes of High Platelet Levels
High platelets are usually a signal, not a disease by themselves. The body increases platelet production as part of a stress or recovery response.
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections frequently raise platelet counts. Clinically, this is a very common finding during or shortly after fever or infection, and levels often normalize on their own.
Inflammation
Chronic inflammatory states—such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel conditions, or long-standing skin and tissue inflammation—stimulate the bone marrow to release more platelets.
Iron Deficiency
One of the most overlooked causes. In iron deficiency, the bone marrow sometimes responds by increasing platelet production. This is why doctors often check iron studies when platelets are persistently high.
Recent Surgery or Injury
After surgery or trauma, platelet levels rise temporarily to support healing and clot formation.
Removal of the Spleen
The spleen normally helps clear older platelets. After splenectomy, higher platelet counts are expected and monitored clinically.
Bone Marrow Disorders (Rare)
Conditions like essential thrombocythemia or other myeloproliferative disorders cause sustained, very high platelet counts and need specialist care.
Chronic Diseases Linked to High Platelet Levels
In long-term illnesses, platelet elevation is often part of ongoing inflammation or altered blood regulation.
- Chronic kidney disease: changes clotting balance and blood regulation
- Liver disease: disrupts normal blood cell control
- Certain cancers: may cause persistent reactive thrombocytosis
- Autoimmune disorders: overactive immune signaling can increase platelets
In these cases, platelet levels usually reflect how active the underlying disease is.
Smoking and Alcohol: How They Affect Platelets
From real-world observation, lifestyle habits matter.
Smoking increases inflammation and blood thickness, which can keep platelet counts on the higher side over time.
Alcohol has a mixed effect. Short-term changes may raise platelets, while long-term heavy intake affects liver and bone marrow function, disturbing normal platelet regulation.
Reducing these exposures often improves blood parameters gradually.
Common Symptoms of High Platelet Levels
Many people with high platelets have no symptoms at all, especially when the cause is secondary. When symptoms do appear, they may include:
- Headache or heaviness in the head
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Chest discomfort
- Visual disturbances
- Warmth, redness, or swelling in limbs
Clinically significant symptoms raise concern mainly when platelet counts are very high or when other risk factors for clotting are present.
How Doctors Think About Reducing High Platelet Levels Naturally
In routine practice, the focus is always on why platelets are high.
For secondary thrombocytosis, natural supportive measures are aimed at helping the body restore balance:
- Adequate hydration helps normalize blood concentration
- Correcting iron deficiency often brings platelets down naturally
- Reducing inflammation through recovery from infection or chronic illness
- Stopping smoking and limiting alcohol improves overall blood quality
- Regular light activity supports circulation
These steps support recovery but are not substitutes for medical evaluation when counts are very high or persistent.
Test Preparation (Quick Practical Notes)
For a platelet or CBC test:
- Fasting is not required
- Normal water intake is advised
- Recent infections, fever, or surgery should be mentioned
- Ongoing medications, especially blood thinners, should be disclosed
Context matters a lot when interpreting platelet results.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical review is important if:
- Platelet count stays above 600,000 per microliter
- High readings are repeated over time
- There are symptoms like chest pain, severe headache, or limb swelling
- There is a history of clotting problems
- Chronic kidney, liver, autoimmune disease, or cancer is present
Persistent or unexplained thrombocytosis always needs proper evaluation.
Important Word Explanations
- Thrombocytosis: High platelet count
- Bone marrow: Tissue where blood cells are produced
- Inflammation: Body’s response to injury or infection
- Dehydration: Reduced body fluid leading to concentrated blood
- Autoimmune disease: Immune system reacting against the body itself
People Also Ask
Is a high platelet count always dangerous?
No. Many cases are temporary and reactive, especially after infection or iron deficiency.
Can platelet levels come down on their own?
Yes. Once the underlying cause improves, platelet counts often normalize naturally.
Does high platelet count always mean a blood cancer?
No. Primary bone marrow disorders are rare. Most cases are secondary.
When do doctors usually worry about high platelets?
Concern increases with very high or persistent counts, or when symptoms suggest clot risk.
Is repeat testing common for high platelets?
Yes. Platelet trends over time help determine whether the rise is temporary or ongoing.
Can lifestyle changes really help?
They help support recovery, but the main focus remains identifying and correcting the cause.
~END~