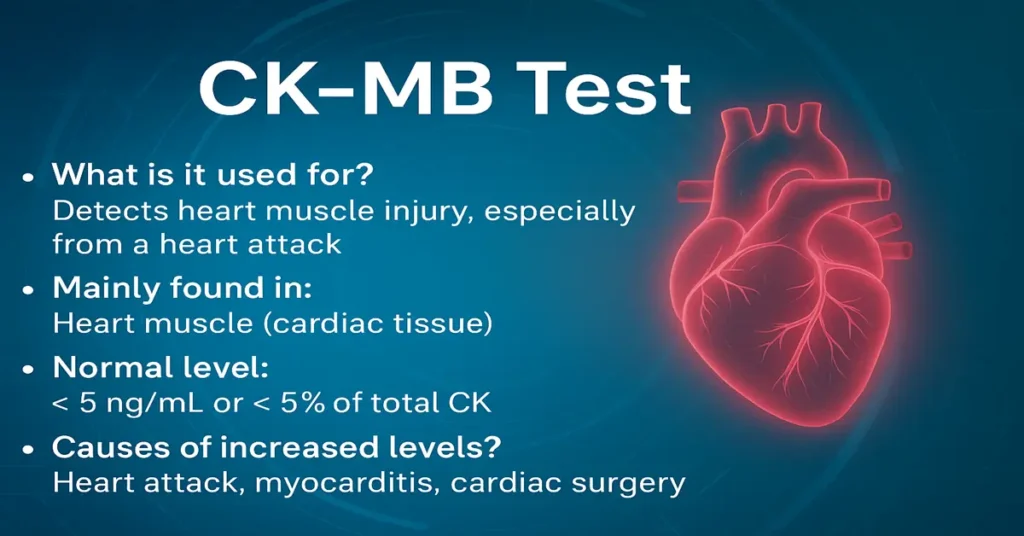
What is the CK-MB Test?
The CK-MB Test (Creatine Kinase–MB Isoenzyme Test) is a blood test that measures the level of the MB fraction of the enzyme creatine kinase in the bloodstream. Creatine kinase is an enzyme involved in energy production, especially in muscle cells that need rapid and continuous energy for contraction.
In the body, creatine kinase exists in three main isoenzymes:
- CK-MM, found predominantly in skeletal muscles
- CK-BB, found mainly in brain tissue
- CK-MB, found primarily in heart (cardiac) muscle
From a clinical standpoint, CK-MB is important because it reflects injury to heart muscle cells. When the heart muscle is damaged, CK-MB leaks into the blood, causing levels to rise within a few hours. For this reason, the test has long been used in the evaluation of suspected heart attacks and other forms of cardiac injury.
Where It Is Produced in the Body
CK-MB is produced mainly within the cells of the heart muscle (myocardium). While very small amounts can also be found in skeletal muscle, its concentration is significantly higher in cardiac tissue.
Because of this distribution, a noticeable rise in CK-MB is generally interpreted as a signal of heart muscle injury rather than routine muscle strain elsewhere in the body. Clinicians always consider this in context with symptoms and other cardiac tests.
Main Functions and Importance
From a biological perspective, CK-MB plays a role in energy handling within heart muscle cells. It helps convert creatine into phosphocreatine, a compound that acts as a quick energy reserve needed for continuous heart contractions.
Clinically, the importance of CK-MB lies less in its metabolic role and more in its value as a cardiac marker. Doctors use it to:
- Support the diagnosis of heart muscle injury, including heart attack
- Estimate the extent of myocardial damage
- Monitor heart muscle injury after cardiac surgery or certain procedures
Although newer markers are now preferred in many settings, CK-MB still provides useful timing information because of how quickly it rises and falls after injury.
Causes of Low or Normal CK-MB Levels
Low or normal CK-MB levels usually indicate that there is no ongoing damage to the heart muscle at the time of testing. In everyday clinical practice, this is a reassuring finding.
Such results are commonly seen in:
- Individuals with a healthy heart
- Patients who have recovered from a past cardiac event
- Situations where heart-related symptoms are due to non-cardiac causes
Symptoms of Low or Normal Levels
Normal CK-MB levels do not produce symptoms. They simply reflect the absence of detectable heart muscle injury in the blood sample taken.
Causes of High or Positive CK-MB Levels
An elevated CK-MB level suggests that heart muscle cells have been injured and released the enzyme into the bloodstream. CK-MB follows a fairly predictable pattern after injury: it rises within a few hours, peaks, and then returns to normal within a couple of days.
Common clinical situations associated with raised CK-MB include:
- Acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), where levels typically rise within 3–6 hours, peak around 12–24 hours, and normalize within 48–72 hours
- Myocarditis, where inflammation damages heart muscle cells
- Cardiac surgery or direct cardiac trauma, which can temporarily increase levels
- Electrical defibrillation, which may cause short-term elevation
- Severe skeletal muscle injury, which can rarely contribute to mild increases
Because of its time-limited rise, doctors may repeat the test to observe the trend rather than rely on a single value.
Symptoms of High CK-MB Levels
When CK-MB is elevated due to heart muscle injury, patients may experience symptoms related to reduced blood flow or cardiac stress. These can include chest discomfort, breathlessness, fatigue, sweating, nausea, dizziness, or irregular heartbeats.
From a clinical perspective, these symptoms—not the lab value alone—drive urgency. CK-MB results are interpreted alongside the patient’s presentation and other investigations.
Reference Ranges
CK-MB is commonly reported either as a concentration or as a percentage of total creatine kinase. Typical reference interpretations include:
- CK-MB (mass method): below the laboratory cut-off is considered normal
- CK-MB percentage of total CK: a low proportion suggests no cardiac injury
Exact cut-off values vary between laboratories, so results are always interpreted using the reporting lab’s reference range.
Sample Type
The test is performed on a venous blood sample, usually collected into a plain tube or serum separator tube.
When heart injury is suspected, samples may be taken more than once over several hours to observe whether CK-MB levels are rising or falling, which provides additional diagnostic clarity.
Test Preparation
No fasting is required for CK-MB testing. Patients are generally advised to avoid heavy or strenuous exercise before the test, as this can affect muscle enzyme levels.
Doctors may also ask about recent injuries, surgeries, or medications, as these details help interpret the result accurately.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical evaluation is important if symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, unexplained sweating, dizziness, or sudden fatigue occur. These symptoms warrant prompt assessment, regardless of test results.
In practice, CK-MB is often measured alongside other cardiac markers, particularly troponins, to build a clearer picture of heart muscle health.
Important Word Explanations
- Creatine Kinase (CK): An enzyme involved in energy production within muscle cells
- Isoenzyme: A different form of the same enzyme found in specific tissues
- Myocardium: The muscular wall of the heart
- Myocardial Infarction: Heart attack caused by blocked blood flow to heart muscle
- Troponin: A highly specific protein marker of heart muscle injury
- Phosphocreatine: An energy-storage compound that supports muscle contraction
~END~
Related Posts
None found