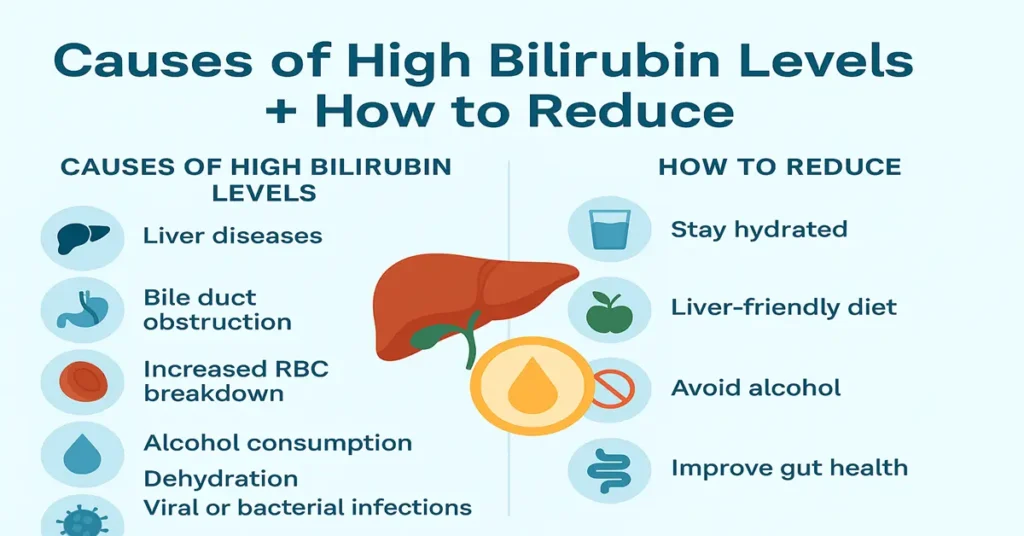
Causes of High Bilirubin Levels + How to Reduce Them Naturally
Overview
Bilirubin is a yellow-colored pigment formed when old red blood cells are broken down in the body. This is a normal, everyday process. The bilirubin produced is carried to the liver, where it is processed and then passed into bile, finally leaving the body through stool and urine.
When this process slows down or gets disturbed, bilirubin starts building up in the blood. Clinically, this shows up as jaundice, with yellowing of the eyes, skin, and dark-colored urine.
It is important to understand that high bilirubin itself is not a disease. In routine lab and OPD practice, it is treated as a signal that something in the liver, bile flow, blood cells, or digestion needs attention.
This article explains the common medical reasons behind high bilirubin, how symptoms usually appear, when natural measures may help, and when the situation becomes serious.
Medical Causes of High Bilirubin (Hyperbilirubinemia)
Liver diseases
The liver is central to bilirubin clearance. When liver cells are inflamed or damaged, bilirubin processing slows down. In practice, this is commonly seen in hepatitis, fatty liver, alcohol-related liver injury, cirrhosis, and autoimmune liver conditions.
Bile duct blockage
If bile cannot flow freely from the liver to the intestine, bilirubin backs up into the blood. Gallstones, narrowing of bile ducts, pancreatic inflammation, or tumors can cause this. Clinically, patients often have pale stools and dark urine along with jaundice.
Hemolysis (increased red blood cell breakdown)
When red blood cells break down faster than normal, bilirubin production increases beyond what the liver can handle. This may occur in hemolytic anemia, certain infections, drug reactions, or inherited red cell disorders.
Gilbert syndrome
This is a common and harmless condition where bilirubin remains mildly elevated due to a minor enzyme deficiency. In lab practice, it is often discovered incidentally and usually does not require treatment.
Alcohol consumption
Alcohol irritates liver cells and interferes with bile flow. Regular alcohol intake is a frequent contributor to raised bilirubin seen during routine testing.
Viral or bacterial infections
Infections such as malaria, dengue, or typhoid can temporarily stress the liver or increase red cell breakdown, leading to higher bilirubin levels.
Inherited conditions affecting bilirubin handling
Rare genetic conditions like Crigler–Najjar, Dubin–Johnson syndrome, and Rotor syndrome affect how bilirubin is processed or excreted.
Medications
Certain drugs, including some antibiotics, steroids, anti-tuberculosis medicines, and hormonal pills, can raise bilirubin levels. This is why doctors usually review medication history when bilirubin is high.
Dehydration and Its Role in High Bilirubin
Dehydration is a commonly overlooked factor. When the body lacks fluids, bile becomes thicker and liver blood flow reduces. This slows bilirubin clearance. In real-world practice, mild bilirubin elevation often improves simply with proper hydration, especially after fever, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Chronic Diseases Linked With High Bilirubin
Chronic liver disease
Long-standing fatty liver, chronic hepatitis, or cirrhosis frequently cause persistent bilirubin elevation.
Pancreatic disorders
Inflammation or swelling of the pancreas can compress bile ducts and obstruct bilirubin flow.
Gallbladder problems
Repeated gallstone episodes may gradually affect bile ducts and raise bilirubin.
Autoimmune conditions
Autoimmune liver disorders interfere with normal bilirubin metabolism over time.
Smoking and Alcohol Effects
Smoking reduces oxygen delivery and increases red blood cell turnover, indirectly raising bilirubin. Alcohol directly damages liver cells and thickens bile. Together, they worsen jaundice and delay recovery in patients with liver stress.
Symptoms of High Bilirubin Levels
Common symptoms
Yellowing of the eyes and skin, dark yellow or brown urine, pale or clay-colored stools, fatigue, nausea, itching, and loss of appetite are commonly reported. Clinically, itching is often an early complaint when bile flow is affected.
Severe symptoms requiring urgent care
Persistent vomiting, abdominal swelling, confusion, or severe abdominal pain suggest serious liver involvement and need immediate medical attention.
How to Reduce High Bilirubin Naturally at Home
Natural measures are helpful only when bilirubin is mildly elevated and the underlying cause is not severe. In moderate or high elevations, medical treatment is essential.
Improve hydration
Adequate fluids support bile flow and liver clearance. Water, oral rehydration solutions, coconut water, and diluted fresh juices are commonly advised.
Support liver-friendly eating habits
Light, easily digestible foods reduce liver workload. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and simple home-cooked meals are usually better tolerated during jaundice episodes.
Limit fatty and oily foods
Heavy, oily meals slow digestion and increase liver stress, often worsening symptoms.
Avoid alcohol completely
Even small amounts can significantly delay bilirubin normalization when liver function is affected.
Avoid smoking
Reducing oxidative stress supports liver recovery.
Support gut health
A healthy gut improves bile metabolism. Simple foods like yogurt, oats, bananas, and fermented foods are often recommended.
Adequate rest
The liver regenerates during rest. In OPD practice, patients who rest adequately often recover faster.
Supplements That May Help (Safe Note)
Some supplements are used under medical supervision to support liver function, such as milk thistle, vitamin B-complex, curcumin, and probiotics. These should never be started without a doctor’s advice and should not replace medical treatment.
When High Bilirubin Becomes Dangerous
Doctors become increasingly concerned as bilirubin rises:
Values above 3 mg/dL with symptoms usually need evaluation.
Levels above 5 mg/dL typically cause visible jaundice.
Readings above 10 mg/dL require hospital assessment.
Very high levels (around 20 mg/dL or more) suggest severe liver failure and are a medical emergency.
Risk increases if jaundice deepens rapidly, urine turns dark brown, stools lose color, or fever and abdominal pain appear.
Test Preparation
For accurate bilirubin testing, fasting for 8–10 hours is usually advised. Alcohol should be avoided for at least 48–72 hours before the test. Inform the doctor about current medications, recent illness, bleeding, or transfusion. Adequate hydration helps ensure reliable results.
When to See a Doctor
Medical consultation is needed if the eyes or skin turn yellow, urine darkens, fatigue becomes severe, appetite drops, fever or abdominal pain develops, or bilirubin rises above 3 mg/dL. People with known liver disease should seek early care, especially if jaundice does not improve.
Important Word Explanations
Bilirubin: Yellow pigment formed during red blood cell breakdown
Jaundice: Yellow discoloration of skin and eyes due to high bilirubin
Hyperbilirubinemia: Elevated bilirubin levels in blood
Hemolysis: Increased breakdown of red blood cells
Bile duct: Channel that carries bile and bilirubin out of the liver
Fatty liver: Excess fat accumulation in liver cells
People Also Ask
Is high bilirubin always a sign of liver disease?
No. It can also occur due to dehydration, infections, blood cell breakdown, or mild genetic conditions.
Can bilirubin levels rise temporarily?
Yes. Fever, illness, dehydration, or certain medications can cause temporary elevation.
Does mild jaundice always need hospital treatment?
Not always. Mild cases are often managed with monitoring, depending on the cause.
When do doctors worry most about bilirubin levels?
Concern increases when levels rise quickly, remain high, or are associated with severe symptoms.
Is repeat bilirubin testing common?
Yes. Repeat tests help track trends and assess recovery or progression.
Can bilirubin return to normal on its own?
In mild, temporary causes, levels may normalize once the underlying issue resolves.
~END~