Causes of High ALP Levels & How to Reduce Them Naturally
Short Overview
ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) is an enzyme produced mainly by the liver and bones, with smaller contributions from the intestines, kidneys, and placenta during pregnancy. In routine lab work, ALP helps doctors understand how well bile is flowing from the liver and how actively bones are remodeling.
A high ALP value is not a diagnosis by itself. In OPD and lab practice, a single raised reading is often seen due to temporary or correctable reasons. However, persistently high ALP or a very sharp rise usually points toward liver, bile duct, or bone-related stress that needs proper evaluation.
Understanding why ALP rises—and how doctors interpret it—helps reduce unnecessary fear and supports timely, sensible action.
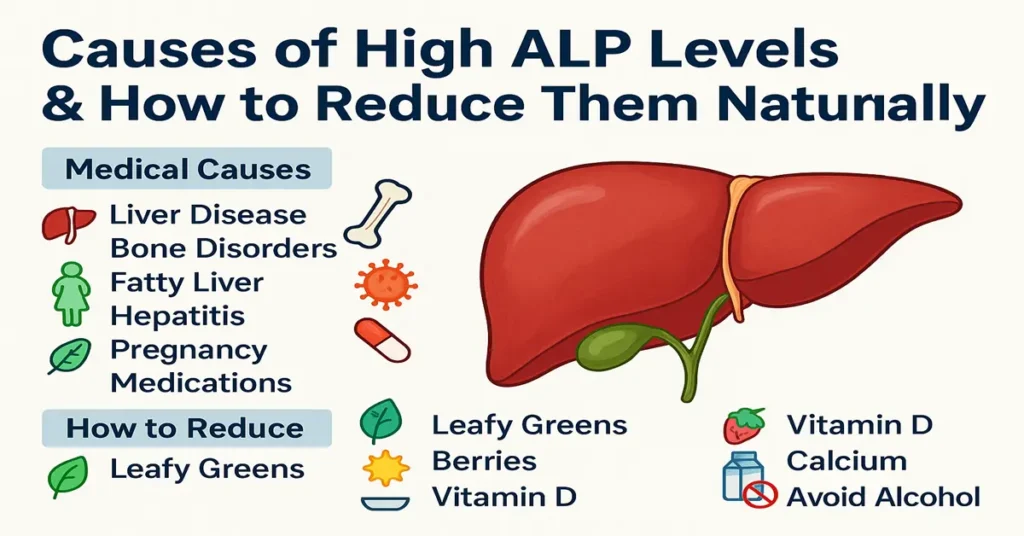
Medical Causes of High ALP Levels
Liver and Bile Duct Disorders
ALP rises prominently when bile flow is disturbed. Clinically, this is one of the first enzymes doctors look at when bile duct problems are suspected.
Common causes include bile duct obstruction, gallstones, liver inflammation, fatty liver disease, liver infections, cysts or tumors compressing bile ducts, primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC).
In routine practice, ALP often rises more than ALT or AST when bile flow is blocked. Doctors usually correlate this with symptoms like jaundice or pale stools.
Bone-Related Conditions
Because bones actively produce ALP, bone conditions can raise levels even when the liver is normal.
These include vitamin D deficiency, osteomalacia, Paget’s disease, healing fractures, hyperparathyroidism, and rapid bone growth in children and adolescents. In children, a high ALP is often physiological, not pathological, due to active bone growth.
Fatty Liver Disease
Both non-alcoholic and alcohol-related fatty liver can raise ALP, especially when inflammation extends beyond simple fat accumulation. In many patients, ALP rises alongside ALT and GGT.
Hepatitis
Viral, autoimmune, or toxin-related hepatitis can increase ALP, though ALT and AST usually rise more prominently. When ALP rises significantly in hepatitis, doctors consider bile duct involvement as well.
Pregnancy
During late pregnancy, ALP naturally increases due to placental enzyme production. This is a normal physiological change unless accompanied by itching, jaundice, or abnormal liver tests suggesting cholestasis of pregnancy.
Intestinal Conditions
Certain intestinal disorders such as celiac disease or chronic malabsorption can mildly elevate ALP. This is often linked to associated vitamin D or mineral deficiencies affecting bones.
Medication Effects
Several medications influence liver or bone metabolism and may raise ALP, including anti-seizure drugs, oral contraceptives, steroids, antibiotics, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and some thyroid-related medicines. In lab practice, medication history is always reviewed before labeling ALP as “disease-related.”
Thyroid Disorders
Hyperthyroidism increases bone turnover and metabolism, which can raise ALP levels even if liver tests are otherwise normal.
Chronic Kidney Disease
In advanced kidney disease, disturbed calcium–phosphorus balance and bone metabolism can lead to elevated ALP. This is often bone-related rather than liver-related.
Dehydration and Its Indirect Role
Dehydration does not directly increase ALP like ALT or AST, but it can worsen underlying problems. Poor hydration affects bile flow, nutrient absorption, and mineral balance, indirectly aggravating ALP elevation.
Chronic Conditions Linked to High ALP
Uncontrolled diabetes, obesity, PCOS, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune diseases can keep ALP mildly to moderately elevated over time. In such cases, ALP reflects ongoing metabolic or inflammatory stress rather than acute disease.
Smoking and Alcohol Effects
Smoking contributes to elevated ALP by increasing inflammation, reducing oxygen delivery, and affecting bone metabolism. Regular smokers often show mildly raised ALP without obvious symptoms.
Alcohol directly irritates liver cells, thickens bile, and worsens fatty liver. In alcohol-related cases, ALP often rises along with AST and GGT.
Symptoms Associated With High ALP
ALP itself does not cause symptoms. Any symptoms come from the underlying condition.
Patients may notice fatigue, weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, right-sided abdominal discomfort, jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, bone pain, joint discomfort, frequent fractures, or unexplained weight loss. When such symptoms appear, ALP elevation usually persists or worsens.
How Doctors Think About Reducing High ALP Naturally
From a clinical perspective, ALP comes down only when the cause improves. Natural reduction focuses on supporting liver function, bone health, and metabolism rather than forcing the number down.
A balanced, liver-friendly diet supports bile flow and reduces inflammation. Adequate vitamin D, calcium, and magnesium intake helps normalize bone-related ALP elevation. Avoiding alcohol is one of the most effective steps when liver involvement is present. Regular moderate physical activity improves both liver health and bone strength. Good hydration supports digestion and bile movement. Smoking reduction improves enzyme balance over time. Managing diabetes, thyroid imbalance, and weight helps stabilize ALP in chronic metabolic conditions.
These measures work gradually and are usually reflected in follow-up tests rather than immediate changes.
When High ALP Becomes Concerning
Doctors become more alert when ALP is consistently more than two to three times the normal range, when it remains high for months, or when it exceeds 400–500 U/L. Such levels may indicate bile duct obstruction, severe liver inflammation, active bone disease, or structural problems like tumors or cysts.
High ALP with jaundice strongly suggests bile flow blockage. High ALP with bone pain or fractures raises concern for vitamin D deficiency or bone disorders. During pregnancy, unexpectedly high ALP with symptoms needs prompt evaluation.
Test Preparation
ALP testing does not require fasting. Avoid alcohol for at least 48 hours, avoid heavy exercise before testing, stay hydrated, and inform your doctor about all medications. Heavy meals just before testing are best avoided.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical review is important if ALP remains high on repeat testing, if jaundice or abdominal pain appears, if there is bone pain or weakness, if ALP is abnormal during pregnancy, if alcohol use is regular, or if chronic conditions like diabetes or thyroid disorders are present. Early evaluation prevents long-term liver and bone complications.
Important Word Explanations
ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase): Enzyme produced mainly by liver and bones
Cholestasis: Reduced or blocked bile flow
Osteomalacia: Bone weakness due to vitamin D deficiency
Hyperparathyroidism: Hormonal condition affecting bone turnover
Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver
Metabolic syndrome: Group of conditions stressing liver and metabolism
People Also Ask
Is a high ALP result always serious?
No. Mild elevations are common and often temporary or nutritional.
Can ALP be temporarily high?
Yes. Pregnancy, bone healing, infections, or medication effects can cause short-term rises.
Does high ALP always mean liver disease?
No. Bones are a common source, especially in vitamin D deficiency or growth phases.
When do doctors usually worry about ALP?
When it stays high over time, rises sharply, or appears with symptoms like jaundice or bone pain.
Is repeat testing common for high ALP?
Yes. Doctors often repeat ALP to see if the elevation is persistent or resolving.
Can ALP return to normal naturally?
In many cases, yes—once the underlying liver, bone, or metabolic issue improves.
~END~

I liked how you added symptoms, causes, and ranges in one place. Very practical for patients like me.
I’m impressed, I need to say. Actually hardly ever do I encounter a weblog that’s both educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you might have hit the nail on the head. Your idea is outstanding; the issue is one thing that not sufficient individuals are talking intelligently about. I am very blissful that I stumbled across this in my search for one thing relating to this.