Cancer Markers
This category collects articles on tumor marker tests used in oncology and clinical practice. Each article describes the specific marker (for example PSA, CA-125, CEA, AFP, CA19-9), why the test is ordered, how to prepare and collect the sample, typical reference ranges, factors that can raise or lower values, and the clinical situations where the marker is useful (screening, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment response, or surveillance). Clear cautions are included — tumor markers rarely confirm cancer on their own and always require clinical correlation and imaging/biopsy when needed. Content is written simply for patients, students, and healthcare professionals.
CA19-9 (Cancer Antigen 19-9) Blood Test – Meaning, Normal Range, and Uses
CA19-9 test helps monitor pancreatic and digestive cancers. Learn about its meaning, normal range, causes of high and low levels,...
Read MoreHLA-B27 Test – Meaning, Uses, Symptoms, Positive vs Negative Results
The HLA-B27 test detects a genetic marker linked to autoimmune diseases like ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, and uveitis. Learn symptoms...
Read MoreLDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) Test – Meaning, Function, Normal Range, and Clinical Importance
The LDH (Lactate Dehydrogenase) test measures an enzyme released during tissue damage. It helps detect heart, liver, lung, and muscle...
Read MoreCEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) Test – Meaning, Function, Normal Range, and Cancer Monitoring
CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen) is a protein used as a tumor marker, mainly for colorectal cancer. This test helps monitor treatment...
Read MoreBeta-hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) Test – Meaning, Function, and Clinical Importance
Beta-hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is a hormone produced during pregnancy and used to confirm and monitor pregnancy health. It also...
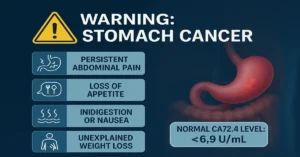
Read MoreCA72.4 (Cancer Antigen 72.4) Blood Test – Meaning, Normal Range, and Uses
CA72.4 test helps detect and monitor stomach, ovarian, and colorectal cancers. Learn its meaning, normal range, and causes of high...
Read MoreChromogranin A (CgA) Test – Purpose, Normal Range, High & Low Level Causes
Learn about the Chromogranin A (CgA) Test, its purpose, procedure, normal range, and causes of high or low levels. Know...
Read MoreCA15-3 (Cancer Antigen 15-3) Blood Test – Meaning, Normal Range, and Importance
CA15-3 test helps monitor breast cancer treatment and detect recurrence. Learn its meaning, normal range, and causes of high or...
Read MoreAFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) Test – Meaning, Function, Normal Range, and Clinical Importance
AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) is a key protein used to detect liver cancer, germ cell tumors, and fetal abnormalities during pregnancy. Learn...
Read MoreJAK2 Mutation Test: Purpose, Symptoms, Results & Simple Guide
Learn about the JAK2 Mutation Test, its role in diagnosing blood disorders, positive vs negative results, symptoms, and when to...
Read MoreBCR-ABL Test – Meaning, Procedure, Normal Range & Results
Know what the BCR-ABL test is, why it’s done, how it helps diagnose and monitor leukemia (CML, Ph+ ALL), normal...
Read MorePSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Test – Meaning, Function, Normal Range, and Clinical Significance
The PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) test measures a protein made by the prostate gland to assess prostate health. It helps detect...
Read More