Overview
CA72.4, also known as Cancer Antigen 72.4 or TAG-72 (Tumor-Associated Glycoprotein 72), is a tumor marker most commonly associated with gastric (stomach) cancer. It may also show elevated values in certain other malignancies, particularly mucinous ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer.
The CA72.4 blood test measures the level of this antigen circulating in the bloodstream. In clinical practice, it is mainly used to support cancer evaluation after diagnosis, assess response to treatment, and monitor for recurrence during follow-up. It is not used as a screening test, as levels can remain normal in early disease and may rise mildly in some non-cancerous conditions.
What is CA72.4?
CA72.4 is a glycoprotein antigen expressed on the surface of certain tumor cells. These cells release the antigen into the blood, where it can be detected by laboratory testing.
Among tumor markers, CA72.4 has particular relevance in gastric cancer, where it can help reflect disease activity. It may also provide useful information in selected cases of ovarian (especially mucinous type) and colorectal cancers.
In laboratory practice, CA72.4 is often interpreted alongside other markers such as CEA and CA19-9. Looking at markers together helps clinicians build a clearer picture rather than relying on a single value.
Where is CA72.4 Produced in the Body?
CA72.4 is mainly produced by malignant cells rather than by normal healthy tissue. Expression is most often seen in:
- Gastric cancer cells
- Ovarian cancer cells, particularly mucinous tumors
- Colorectal cancer cells
Less commonly, it may be detected in pancreatic or lung cancers.
In healthy individuals, CA72.4 levels are typically very low or undetectable.
Functions and Clinical Importance of CA72.4
CA72.4 does not have a known role in normal body function. Its value lies entirely in its clinical use as a tumor marker.
1. Gastric Cancer Marker
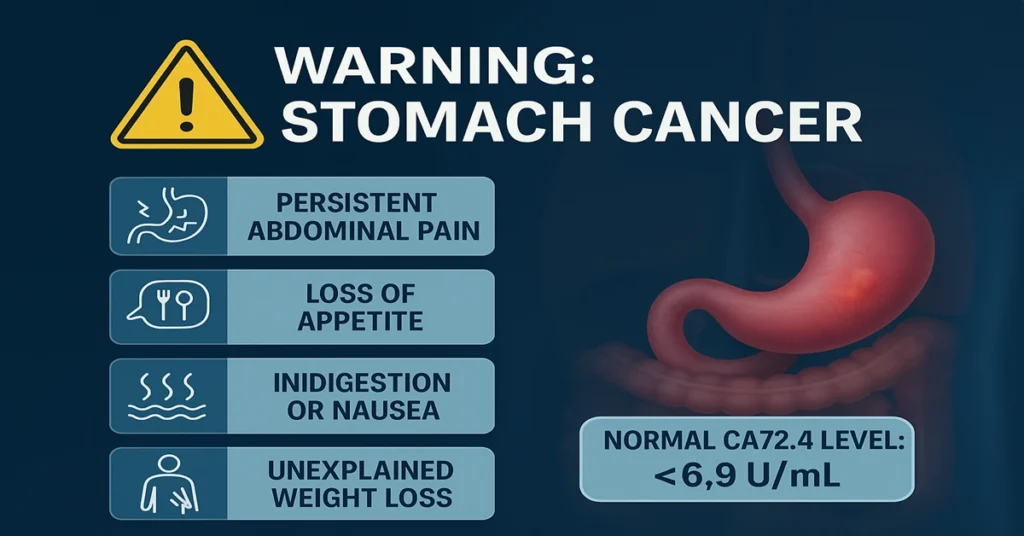
The most established role of CA72.4 is in stomach cancer. It can support diagnosis after suspicion is raised and is useful for tracking disease burden over time.
2. Ovarian Cancer (Mucinous Type)
In mucinous ovarian tumors, CA72.4 may be assessed alongside CA125 to provide additional diagnostic context, particularly when imaging findings are unclear.
3. Treatment Response Indicator
Changes in CA72.4 over time are often more meaningful than a single reading. Falling levels during or after therapy generally suggest reduced tumor activity, while rising values may indicate persistent or returning disease.
4. Combined Marker Use
CA72.4 is frequently evaluated together with CEA and CA19-9 in gastrointestinal cancers. This combined approach improves clinical confidence and reduces the risk of misinterpretation.
Causes of Low or Normal CA72.4 Levels
Low CA72.4
Low or undetectable CA72.4 levels are common in healthy individuals.
In patients with known cancer, stable or decreasing levels after treatment usually indicate good disease control.
Symptoms of Low Levels
There are no symptoms linked to low CA72.4 values.
Such results are generally reassuring and suggest minimal tumor marker activity.
Causes of High CA72.4 Levels (Elevated CA72.4)
Cancer-Related Causes
Elevated CA72.4 levels may be seen in:
- Gastric (stomach) cancer
- Ovarian cancer, especially mucinous type
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Lung cancer (uncommon)
Among these, the strongest association is with gastric cancer.
Non-Cancerous (Benign) Causes
Although CA72.4 is relatively specific, mild elevations can occur in some benign conditions, including:
- Liver cirrhosis
- Benign ovarian cysts
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Chronic gastritis
In such cases, elevations are usually modest and transient.
Symptoms of High CA72.4 Levels
CA72.4 itself does not cause symptoms. Any symptoms present are due to the underlying condition. Depending on the cause, these may include:
Gastric-related symptoms
- Persistent upper abdominal discomfort
- Indigestion or nausea
- Early fullness after meals
- Reduced appetite or unexplained weight loss
Ovarian or colorectal-related symptoms
- Pelvic discomfort or bloating
- Changes in bowel habits
- Ongoing fatigue
Persistent or progressive symptoms should always be evaluated further.
Reference Range (Normal Blood Levels)
- Normal: < 6.9 U/mL
- Mild elevation: 7 – 20 U/mL
- High elevation: > 20 U/mL
Reference ranges may vary slightly between laboratories. Interpretation should always consider trends over time and be correlated with imaging and clinical findings.
Sample Type and Testing Details
- Sample Type: Blood (serum)
- Tube Used: Red-top (plain) tube
- Fasting Required: Not required
- Result Time: Usually 1–2 days
In oncology follow-up, CA72.4 testing is often repeated at intervals to monitor changes rather than relied upon as a one-time result.
Test Preparation
No special preparation is required.
It is helpful to inform the doctor about recent surgery, ongoing cancer treatment, or known stomach or liver conditions, as these factors may influence interpretation.
When to Consult a Doctor
Medical review is recommended if you experience:
- Persistent abdominal discomfort or bloating
- Difficulty eating or early fullness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Ongoing nausea or vomiting
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
If CA72.4 levels remain elevated or show a rising trend, further evaluation may include imaging studies, additional tumor markers, or tissue biopsy, depending on the clinical situation.
Important Word Explanations
- Tumor Marker: A substance measured in blood that may rise in certain cancers or disease states
- Glycoprotein: A protein with attached sugar molecules, often found on cell surfaces
- Malignant: Cancerous and capable of spreading
- Benign: Non-cancerous condition
- Metastasis: Spread of cancer from its original site to other organs
- Recurrence: Return of cancer after treatment
- TAG-72: Tumor-Associated Glycoprotein 72, the molecule detected by the CA72.4 test
~END~
Related Posts
None found