What is Vitamin B7 (Biotin)?
Vitamin B7, also known as Biotin or Vitamin H, is a water-soluble vitamin that belongs to the B-complex family.
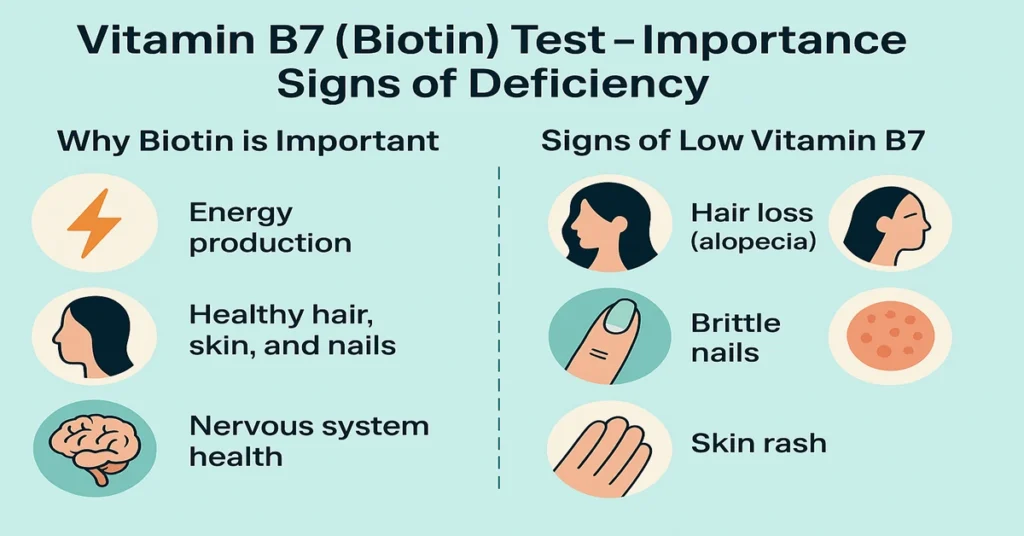
It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into energy — by helping the body break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Biotin is often called the “beauty vitamin” because it supports healthy hair, skin, and nails.
In addition to its cosmetic benefits, Vitamin B7 also contributes to brain health, metabolism, and nerve function.
Where is Vitamin B7 Produced in the Body?
The human body cannot make enough Biotin on its own.
We mainly obtain it through dietary sources, such as eggs, milk, nuts, seeds, whole grains, sweet potatoes, and leafy vegetables.
A small amount of Biotin is also produced by gut bacteria in the intestines, but this quantity is not sufficient to meet daily body requirements.
Hence, regular intake through food or supplements is necessary.
Main Functions and Importance of Vitamin B7
Vitamin B7 is involved in multiple biochemical and metabolic functions in the body.
1. Energy Production
Biotin acts as a coenzyme in reactions that convert carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids into energy.
This makes it essential for the body’s overall energy metabolism.
2. Healthy Hair, Skin, and Nails
It supports keratin production, a structural protein that keeps hair, skin, and nails strong and healthy.
Low Biotin levels can cause hair thinning or brittle nails.
3. Nervous System Health
Vitamin B7 contributes to the proper functioning of the nervous system by supporting neurotransmitter activity and brain signal transmission.
4. Blood Sugar Regulation
It helps in glucose metabolism and supports insulin function, assisting in blood sugar balance.
5. Gene Regulation
Biotin also plays a role in gene expression, DNA replication, and cell growth, making it vital for tissue repair and healthy cell function.
Causes of Low Vitamin B7 Levels (Deficiency Causes)
Biotin deficiency is uncommon but can happen under certain conditions:
- Poor dietary intake or prolonged fasting
- Consuming raw egg whites regularly (they contain avidin, a protein that binds to Biotin and prevents its absorption)
- Long-term use of antibiotics, which kill beneficial gut bacteria that produce Biotin
- Genetic disorders, especially biotinidase deficiency, which prevents recycling of Biotin in the body
- Chronic alcoholism or liver disease, leading to poor absorption
- Pregnancy, due to increased nutritional demand
Symptoms of Vitamin B7 Deficiency
Low Biotin levels can cause visible physical and neurological symptoms, such as:
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Dry, red, or scaly skin rash, especially around the eyes, nose, or mouth
- Brittle nails that break easily
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Mood changes, depression, or hallucinations due to nerve involvement
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet (neuropathy)
- In infants: delayed development, seizures, or low muscle tone (hypotonia) in severe cases
If not treated, deficiency can gradually worsen and affect both the nervous system and skin health.
Causes of High Vitamin B7 Levels
Excessive levels of Biotin are rare and usually occur only from over-supplementation.
The body naturally removes excess Biotin through urine, as it is water-soluble.
However, taking very high doses (10–100 times the recommended level) may interfere with certain lab tests.
Symptoms of High Vitamin B7 (Toxicity)
There are no known serious toxicity effects from Biotin intake.
However, too much Biotin can cause false lab test results, especially in:
- Thyroid tests (can show false high or low thyroid levels)
- Cardiac troponin tests (can interfere with heart attack diagnosis)
Always inform your doctor if you are taking Biotin supplements before any lab test.
Reference Range (Normal Blood Levels)
| Parameter | Normal Range |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B7 (Biotin) | 200 – 1200 ng/L (may vary slightly by laboratory) |
Levels below 200 ng/L may indicate deficiency, while higher levels are usually related to supplementation.
Sample Type and Test Method
- Sample type: Blood (serum or plasma)
- Purpose: To measure Biotin concentration in the body.
- Fasting: Usually not required, unless other tests are being conducted at the same time.
Test Preparation
To ensure accurate results:
- Avoid Biotin supplements for at least 48–72 hours before the test.
- Inform your doctor about any medications or multivitamins you take.
- Follow general good practices — stay hydrated and avoid fasting unless instructed.
- Get your test done in the morning for stable readings.
When to Consult a Doctor
Consult your healthcare provider if you notice:
- Sudden hair loss or brittle nails
- Dry, red, or scaly skin
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Fatigue, low mood, or nerve symptoms
- If you are pregnant, or using Biotin supplements and notice changes in skin or test results
Your doctor may suggest:
- A Biotin test to confirm levels
- Dietary changes or Biotin-rich foods
- Supplements if required, in safe dosages
Important Word Explanations
| Word | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Biotin / Vitamin B7 | A water-soluble B-complex vitamin needed for energy and healthy hair, skin, and nails. |
| Avidin | A protein in raw egg whites that binds Biotin and prevents its absorption. |
| Biotinidase Deficiency | A rare genetic disorder that prevents the body from reusing Biotin. |
| Neuropathy | Nerve-related condition causing numbness or tingling in extremities. |
| Hypotonia | Low muscle tone, seen especially in infants with severe deficiency. |
~END~