Introduction
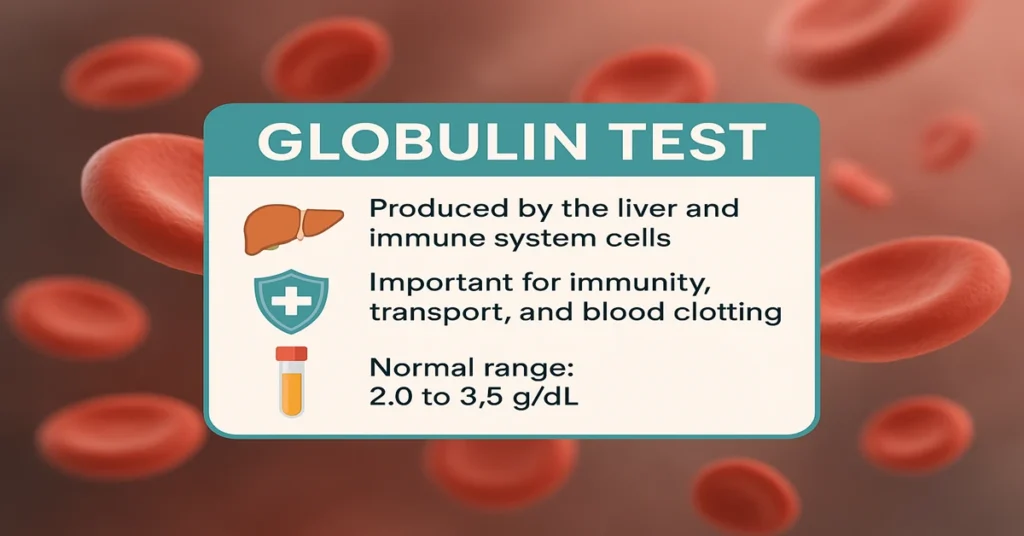
Proteins are essential for body function, and globulins form an important group of these proteins in the blood. Unlike albumin, which is a single protein, globulin refers to a family of proteins with multiple roles, especially in immunity, transport, and inflammation control.
The Globulin Test measures the total amount of globulins in the blood and is usually performed along with the Total Protein Test and the Albumin/Globulin (A/G) Ratio Test. Together, these provide valuable information about a person’s liver function, kidney health, immune system, and potential presence of cancers or chronic diseases.
What is Globulin?
Globulin is a collective term for several proteins present in blood plasma. These proteins are involved in:
- Fighting infections
- Carrying nutrients and hormones
- Regulating inflammation and clotting
The Globulin Test helps detect abnormalities in these proteins, making it useful in diagnosing immune deficiencies, chronic diseases, and liver or kidney problems.
Where is Globulin Produced in the Body?
Globulins are made in different parts of the body depending on their type:
- Alpha and Beta Globulins – Produced by the liver.
- Gamma Globulins (Immunoglobulins/antibodies) – Produced by immune system cells, especially plasma cells and lymphocytes.
Functions and Importance of Globulins
Globulins play diverse and vital roles:
- Immunity
- Gamma globulins include antibodies such as IgG, IgA, IgM, which defend the body against infections.
- Transport of Substances
- Alpha and beta globulins carry:
- Hormones
- Lipids (fats)
- Iron (via transferrin)
- Vitamins
- Alpha and beta globulins carry:
- Blood Clotting and Inflammation
- Certain globulins assist in clotting and regulate inflammation.
- Medical Importance
- Abnormal globulin levels can point to:
- Immune disorders
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Certain cancers such as multiple myeloma or lymphoma
- Abnormal globulin levels can point to:
Causes of Low Globulin (Hypoglobulinemia)
A reduced globulin level may indicate one or more of the following:
- Liver disease (less protein production).
- Kidney disease (protein loss in urine).
- Immune deficiency disorders, e.g., agammaglobulinemia.
- Malnutrition or poor absorption (e.g., celiac disease).
- Cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma.
- Long-term steroid use, which suppresses immune function.
Symptoms of Low Globulin
When globulin levels are low, the body becomes vulnerable. Symptoms may include:
- Frequent infections due to poor immunity.
- Chronic fatigue or weakness.
- Swelling or edema, especially if total protein is also low.
- Delayed wound healing.
- Muscle loss or weakness over time.
Causes of High Globulin (Hyperglobulinemia)
High globulin levels may occur when the body is fighting infection or producing abnormal proteins. Common causes are:
- Chronic infections such as tuberculosis or hepatitis.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Blood cancers – Multiple myeloma or Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia.
- Liver disease, including cirrhosis, which increases globulin as liver function declines.
- HIV/AIDS, due to overactivation of the immune system.
Symptoms of High Globulin
Symptoms depend on the underlying condition. They may include:
- Bone pain or fractures (especially in multiple myeloma).
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Fever or night sweats.
- Enlarged lymph nodes or spleen in cases of cancers or immune activation.
Reference Range (Normal Values)
- Globulin: 2.0 to 3.5 g/dL
(May vary slightly depending on the laboratory.)
Formula:
Globulin = Total Protein – Albumin
Often, doctors use the Albumin/Globulin (A/G Ratio) to compare levels of the two proteins. A disturbed ratio may suggest specific conditions like autoimmune disease, chronic infection, or myeloma.
Sample Type and Collection
- Sample Type: Serum
- Tube Used: Red Top (Plain Tube)
This is a routine blood test and does not usually require fasting, unless paired with other tests.
Test Preparation
- No special preparation is required.
- Inform your doctor about medications, especially steroids or immunosuppressants.
- If this test is part of a liver or kidney panel, fasting may be requested.
When to Consult a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if you have:
- Repeated or severe infections.
- Unexplained fatigue or weight loss.
- Swelling, fluid retention, or edema.
- Bone pain or frequent fractures.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, fever, or night sweats.
Important Word Explanations
- Globulin – A group of blood proteins involved in immunity, transport, and inflammation.
- Hypoglobulinemia – Low globulin levels in the blood.
- Hyperglobulinemia – High globulin levels in the blood.
- Immunoglobulins – Antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM, etc.) that fight infections.
- A/G Ratio – Albumin to globulin ratio, useful in diagnosing liver, kidney, or immune disorders.
- Multiple Myeloma – A type of cancer of plasma cells that causes abnormal protein production.
~END~